Aruba IoT Configuration Guide
This document describes the principals and configuration of the Aruba IoT integrations using ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.8.0.0 or higher.
Table of contents
Aruba IoT concepts
Aruba, a Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) company supports IoT applications based on Wi-Fi (e.g. Wi-Fi tracking), BLE (e.g. asset tracking or sensor monitoring), ZigBee and 3rd party protocols via USB-extension by providing the connection layer using Aruba access points. IoT devices can send/receive data via the Aruba APs built-in radios or supported 3rd party radios connected via USB to 3rd party backend systems.
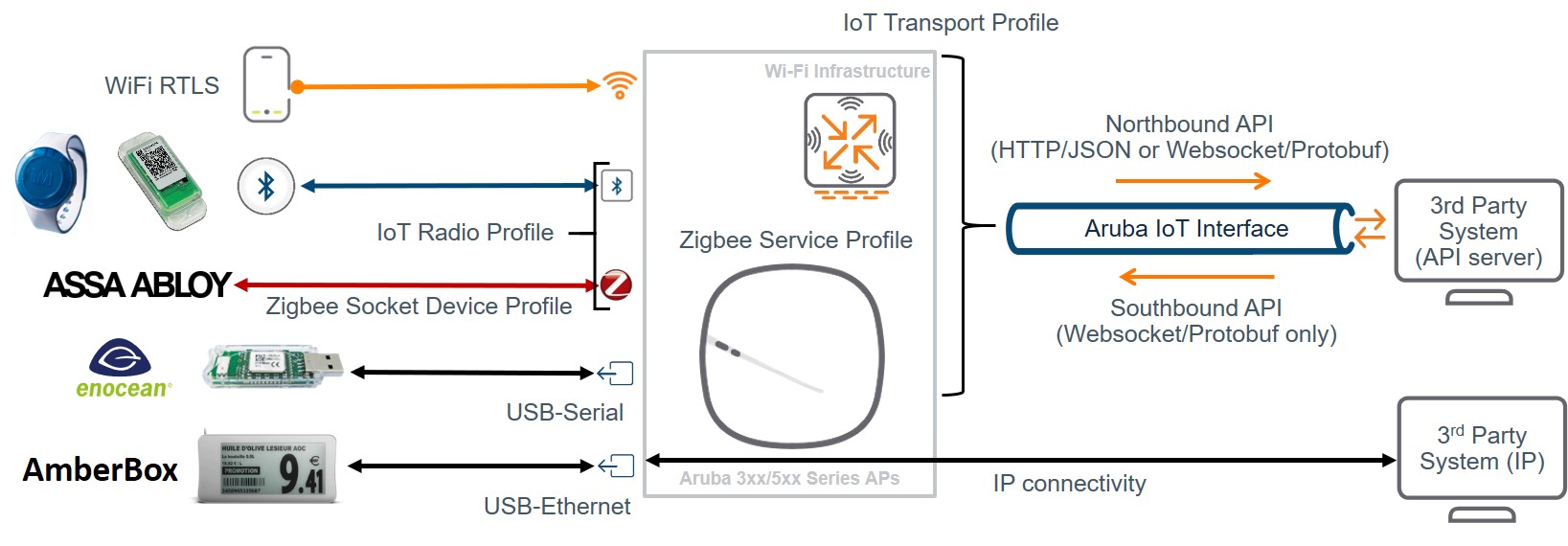
The Aruba AP radios can be used as transmitter/receiver (e.g. BLE connect, ZigBee) or just as a receiver/sensor (e.g. BLE asset tracking, Wi-Fi tracking), depending on the respective IoT solution. With that the AP provides a one-way or two-way communication channel between IoT devices (e.g, sensors, actors) and IoT backend systems.
The access point works as a protocol translational gateway between the different IoT radios/protocols and the Aruba IoT server interface protocol or plain IP protocol depending on the respective IoT solution being used.
IoT connectivity (radio-side)
On the radio-side the Aruba access points support different IoT radio technologies either though integrated radios or 3rd party solutions connected to the APs USB port.
Wi-Fi
The Aruba access point Wi-Fi radios can be used to forward associated/unassociated client information and RTLS data for Wi-Fi based tracking use cases. Wi-Fi client and RTLS data is encapsulated in the Aruba IoT server interface protocol and forwarded to the IoT backend system.
Aruba IoT radio
An Aruba IoT radio is an additional internal or external radio in the Aruba AP-3xx/5xx series access points that can be leveraged for IoT connectivity.
A single Aruba AP-3xx/5xx series access points can support up to two IoT radios, one internal and one external. This would allow to use one radio e.g. for BLE and the other one for ZigBee concurrently.
The access point removes/adds the radio specific headers from/to IoT devices e.g. BLE or ZigBee and forwards/receives the data payload encapsulated in the Aruba IoT server interface protocol to/from the IoT backend system.
Internal
Aruba AP-3xx/5xx series access points provide an integrated Aruba IoT radio for the IoT connectivity supporting the following radio technologies:
- AP-3xx: BLE4 (Gen1)
- AP-5xx: BLE5/802.15.4 (Gen2) e.g. ZigBee
BLE Wi-Fi Co-Existence
Starting with ArubaOS/Instant OS version 8.8.0.0 BLE Wi-Fi Co-Existence has been introduced to improve the overall WLAN and BLE receiver performance and to prevent inter-modulation by coordinating WLAN and BLE traffic and avoiding WLAN and BLE transmitting simultaneously. The feature is enabled by default.
Note:
BLE Wi-Fi Co-Existence is only supported on Aruba AP-53x and AP-55x series access point series for the internal Aruba IoT Gen2 radio. The Aruba AP-505H hospitality accdess point series has some internal HW-based filtering to compensate local interference that works differently to the BLE Wi-Fi Co-Existence feature.
External
In addition to the internal IoT radio Aruba also provides an IoT expansion radio that supports the same radio technologies as the AP-5xx series internal IoT radio:
- Aruba IoT Expansion Radio = BLE5/802.15.4 (Gen2) e.g. ZigBee
The intention of the Aruba IoT expansion radio is to add the 802.15.4(ZigBee) capability to the AP-3xx series access points.
Note:
The internal and the expansion BLE5/802.15.4 (Gne2) IoT radio can be enabled to run BLE and ZigBee concurrently. But in this case the IoT radio can only transmit but not receive BLE packets, while the ZigBee communication works bi-directional.This allows enabling the APs BLE console as well as BLE beaconing (iBeacon) for indoor navigation use cases in parallel to ZigBee use cases. But BLE tracking uses cases like asset tracking are not supported in this case.
In order to support BLE tracking or bi-directional use cases concurrently to ZigBee uses cases on the same access points two Aruba IoT radios Gen2, one internal and one external, are required. The external radio should be used as ZigBee radio in this case. Therefore this scenario is currently only supported on the Aruba AP-5xx series access points.
The configuration of the Aruba IoT radios is handled in the IoT radio profile configuration.
USB/3rd party IoT radio’s
Aruba supports the expansion of Aruba access points using the AP’s USB port with supported 3rd party radio solutions. Depending on the particular solution the integration uses one of the following methods:
- USB-to-serial
- USB-to-ethernet
In all cases the USB connected host system removes/adds the radio specific headers/protocols from/to IoT devices and forwards/receives the data payload to the access point using one of the USB methods.
Supported USB connected devices does not required a specific configuration, except for vendor specific implementations, but it can be controlled which USB devices are allowed to connect to an access points. This can be controlled using the AP USB device management.
USB-to-serial
The 3rd party solutions using the USB-to-serial method forwards the data payload to/from the access point using serial-data. The Aruba access point encapsulates the serial-data payload in the Aruba IoT server interface protocol to/from the IoT backend system.
Note:
No specific configuration is required for USB-to-serial devices. Serial data is only forwarded though the Aruba IoT server interface, if enabled in the server-side configuration.
USB-to-ethernet
The 3rd party solutions using the USB-to-ethernet method provides ethernet/IP connectivity to the connected USB host system. The USB host system is connected to the access point in the same way as a wired ethernet client. No data processing is done by the access point and ethernet/IP data packets form the USB host system is forwarded like any other ethernet/IP traffic.
Vendor specific implementations
The following vendor specific USB integrations do not follow the previously mentioned methods and require a dedicated configuration.
IoT server connectivity (server-side)
On the server-side IoT data payloads are either forwarded directly by USB-to-ethernet connected devices using IP transport or using the Aruba IoT server interface providing different transport protocols and data encapsulations.
USB-to-ethernet connectivity only requires applying a Wired-Port profile to the APs USB port to give the USB host system ethernet/IP access. The benefit of this approach is that USB host system’s network access can be separated from the AP management networks e.g. by assigning a different VLAN and can be controlled using the AP integrated firewall like any other wired ethernet client connected to the AP. The USB host system uses its own IP stack with a separate IP address for its communication to the remote IoT system.
Note:
Vendor specific USB implementations like SES Imagotag Electronic Shelf Labels (ESL) are using IP transport with a vendor specific configuration.
Aruba IoT server interface
The Aruba IoT server interface is an Aruba proprietary server-side connectivity interface to connect to IoT servers using the Aruba AP’s or Aruba controllers management IP address. The interface provide multiple transport protocol and data encapsulation options and is specified in the Aruba IoT Server Interface Guide.
All Aruba IoT server interface related aspects are configured in an iot transport profile.
Note:
Up to 4 iot transport profiles can be concurrently enabled per Aruba Instant AP or ArubaOS AP group.
This allows to run up to 4 IoT applications concurrently on an Aruba access point ,e.g. Aruba Meridian Beacon Management + Aruba Meridian Asset Tracking + 3rd Party BLE Asset Tracking + EnOcean.
The following chapters describe the Aruba IoT server interface related options and services.
Server connection types
The Aruba IoT server interface supports vendor specific and generic server connections types.
The following generic connection types allow IoT data forwarding for the different IoT connectivity (radio-side) options previously described.
Telemetry-Https
The Telemetry-Https connection type can be use to send BLE telemetry reports in one direction only, from the radio-side to the server-side, using HTTP POST requests.
This connection type can be used for BLE-based asset tracking or sensor monitoring use cases using easily consumable JSON data. The used JSON data structure is defined in the Aruba IoT Telemetry JSON Schema.
Note:
Telemetry-Https is only meant to be used for low thoughput application/use cases with a low amount of APs (<20) and a high report intervall (>60 s). Trying to use Telemetry-Https for low latency/high toughput use cases may BLE mesages beeing dropped/delayed. Please only use Telemetry-Websocket for low latency/high toughput use cases.
Note:
Starting with ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.6.0.0 or higher no new BLE device classes will be added to be used with Telemetry-Https.
Telemetry-Websocket
The Telemetry-Websocket connection type can be used for all supported IoT transport services providing a bi-directional communication channel though a web socket (ws) or secure web socket (wss) connection.
Communication via the Telemetry-Websocket connection is encoded using the Google Protocol Buffers serialization protocol. Supported messages types (northbound/southbound API) and the encoding and decoding of the data payloads is defined in the Aruba IoT Protobuf Specification.
This connection type enables the full set of IoT connection capabilities of an Aruba infrastructure.
Note:
The IoT-Utilities app only supports Telemetry-Websocket connections.
Azure-IoTHub
The Azure-IoTHub connection type can be use to send/receive BLE data forwarding/Serial-data directly to Azure IoT Hub by using the AMPQ over websocket protocol.
With this connection type Aruba controller’s or Aruba Instant access points work as a protocol translation gateway (in Azure terms) to send data to Azure IoT Hub on behalf of connected IoT devices.
For details please see the Azure IoT Hub Integration Tech Note
Server connection encryption
Even if un-encrypted HTTP or web socket connectivity is supported by the Aruba IoT server interface, it is recommended to only use encrypted connections to remote IoT systems.
In order to establish secure web socket (wss) or HTTPS connections the remote server’s self-signed certificate or root CA certificate has to be added to the Aruba controller/Aruba Instant access points trusted CA list.
Note:
If the IoT server certificate is un-trusted the server connection will not be established.
Please refer to importing certificates for how to add/import required certificates on the Aruba infrastructure.
Note:
The IoT-Utilities app provides a download link on the web dashboard to download the self-signed server certificate. Alternatively a certificate signed by a private or public CA certificate that is trusted by the Aruba infrastructure can be installed into the app.
Authentication and authorization
Depending on the Aruba IoT server connection type different authentication and authorization methods are supported/required to establish server-side connections.
Supported authentication and authorization methods are:
- static access token
- username/password
- client_id/secret
Details about the different authentication methods are documented in the Aruba IoT Server Interface Guide.
Connection management
Server connections are established form every single Aruba Instant access point, in case of a controller-less setup, or from every Aruba controller in case of a controller-based setup.
For example, in a controller cluster setup with 4 controllers every controller will establish a connection to the remote server.
Note:
In an ArubaOS controller setup the number of server connections equals the number of controllers.In an Aruba Instant setup the number of server connections equals the number of APs.
In a controller based setup IoT data is forwarded to/from the remote IoT server via the APs active controller only. In case of a failover the IoT communication will also failover to the backup controller’s IoT interface connection.
Note
Redundant controller based setups requires proper connection management on the IoT server side for bi-directional communication to continue to work in case of a failover. The remote server application has to keep tack of which AP and IoT radio is reachable via which connection.For details please refer to the Aruba IoT Server Interface Guide.
IoT transport services
The Aruba IoT server interface supports different transport services for the IoT communication.
The usage of the specific transport service depends on the used IoT connectivity and IoT server connection type.
Note: Not all transport services are supported with every available IoT server connectivity option.
To enable one or multiple transport services the corresponding supported device class filter has to be enabled in the iot transport profile configuration.
The table below shows a summary of the available transport services and the corresponding supporte server connection types and device class filter:
Note:
For details about the available data payloads and the correspondig encoding and deconding of the different IoT transport servcies please refer to the Aruba IoT Server Interface Guide.
Wi-Fi telemetry
Wi-Fi telemetry sends periodic reports (northbound only) about all the Wi-Fi devices that are discovered by an AP.
Note:
For an AP to discover Wi-Fi devices the AP radios has to be enabled and set to access or monitor mode.
Wi-Fi devices are classified either as:
- associated (wifi-assoc-sta)
- unassociated (wifi-unassoc-sta)
At every reporting interval the following information are reported:
- station MAC address
- received signal strength (RSSI)
- device class
Wi-Fi telemetry is enabled using the device class wifi-assoc-sta and/or wifi-unassoc-sta in the iot transport profile configuration.
Note:
WiFi telemetry is only available when using the IoT server connection type Telemetry-Websocket.
Wi-Fi RTLS data forwarding
WiFi RTLS data forwards the wireless data frames that originate from unassociated Wi-Fi tags addressed to a configured RTLS destination MAC address to the remote server.
Wi-fi devices matching this traffic pattern are classified as wifi-tags.
The RTLS destination MAC address has to be set in the iot transport profile configuration.
Wi-Fi frames matching the RTLS destination MAC address are immediately forwarded via the IoT server connection (northbound only) to the remote server including the following information:
- received signal strength (RSSI)
- device class (set to “wifi-tag”)
- payload of the wireless frame
Wi-Fi RTLS data forwarding is enabled using the device class wifi-tag in the iot transport profile configuration.
Note:
WiFi telemetry is only available when using the IoT server connection type Telemetry-Websocket.
BLE telemetry
BLE telemetry sends periodic reports about all BLE devices that are discovered by an AP’s IoT radio and saved on a local BLE table to a remote server.
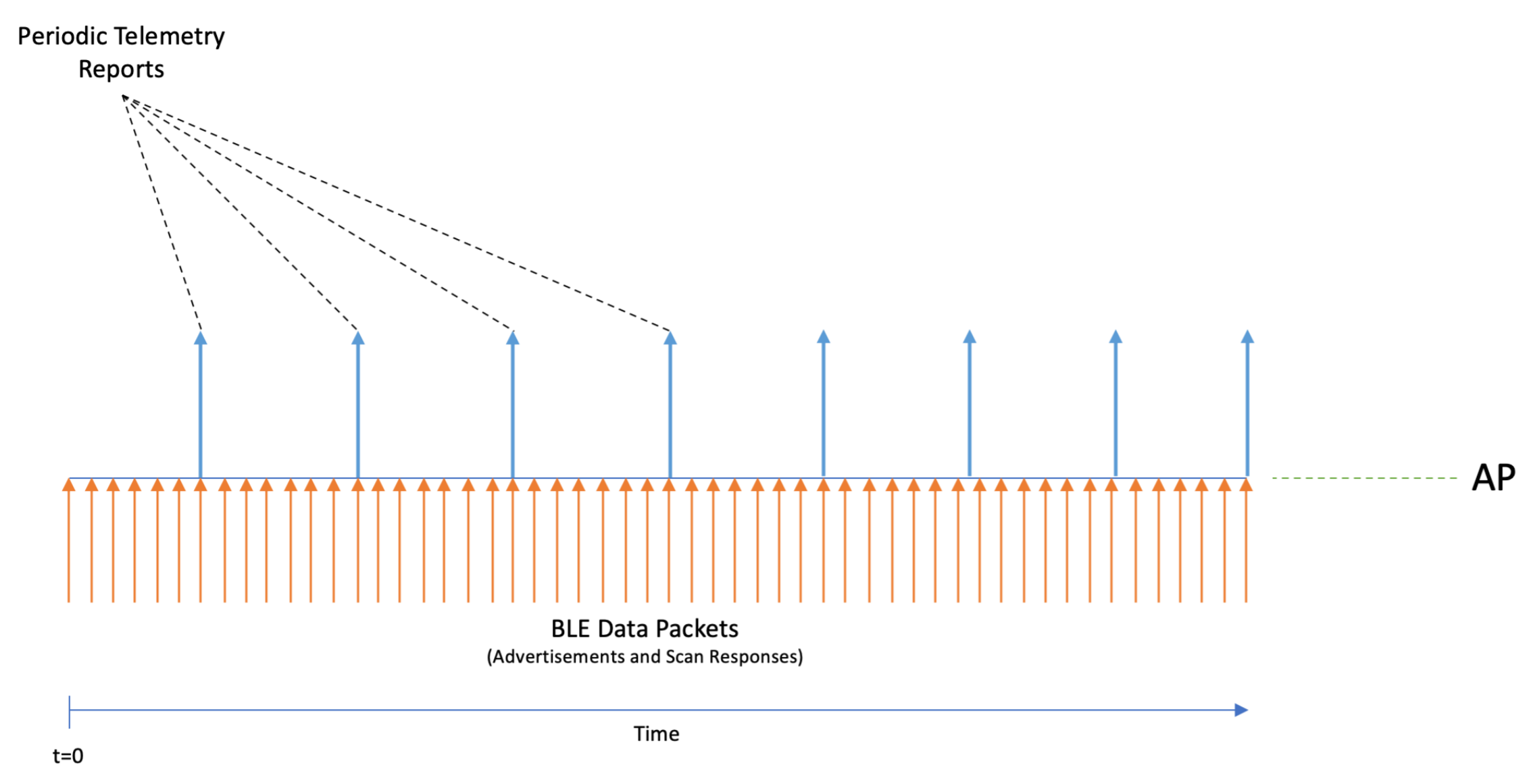
The AP will continuously listen for advertisements and scan responses and parse/decode these packets for supported BLE protocols. The APs BLE table is updated and reported as BLE telemetry data at a configurable report interval.
BLE table limits:
- max: 512 devices per AP
- Oldest entries are deleted first (FIFO)
These telemetry reports contain a summary of all the BLE devices that are seen by a particular AP. For each individual BLE device the supported protocol information will be reported. For unsupported BLE protocols at least the BLE MAC address and the RSSI value are reported.
An example of these reports and the JSON schema can be found in the Aruba IoT Telemetry JSON Schema documentation.
BLE telemetry is enabled for the selected BLE device class in the iot transport profile configuration.
Note:
BLE Telemetry is the default data forwarding mode for all BLE device classes and cannot be disabled.
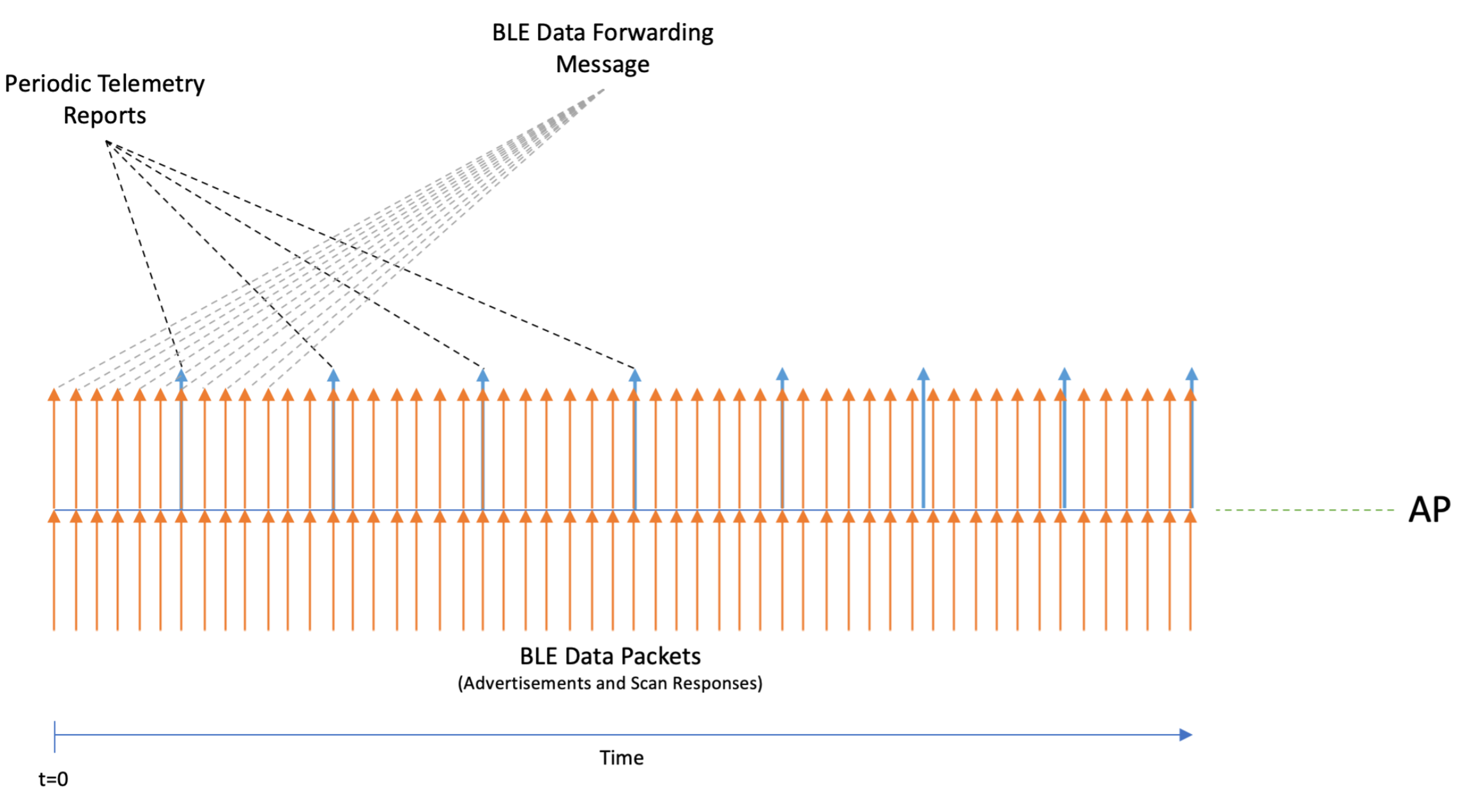
BLE data forwarding
BLE data forwarding sends all BLE advertisement and scan response frames from known BLE vendor device classes to a remote server.
BLE data forwarding works by forwarding the raw BLE data packets to the remote server immediately when they are received by the AP’s IoT radio.
Important:
BLE forwarding increase the amount of server-side traffic because a message for every BLE advertisement and scan response from eligible BLE devices is forwarded.
Furthermore, BLE data forwarding happens in addition to the periodic telemetry reporting. Both methods happen in parallel.
Therefore, if BLE data forwarding is the main method for the IoT use case it is recommended to set a high reporting interval in the iot transport profile.
With ArubaOS/Instant version 8.7.0.0 no special configuration is needed to enable BLE data forwarding. The BLE data service is automatically enabled for the following selected device classes:
- mysphera
- abilitySmartSensor
- sBeacon
- exposureNotification
- wiliot
Starting with ArubaOS/Instant version 8.8.0.0 BLE data forwarding is supported for all known BLE vendor device classes, except for BLE device class all or unclassified.
BLE data forwarding is enabled for the selected BLE device class in the iot transport profile configuration.
Note:
BLE data forwarding is only available when using the IoT server connection type Telemetry-Websocket.
BLE connect
BLE connect provides functions to connect and interact with BLE devices remotely via the Aruba IoT server interface using the BLE GATT profile.
This allows IoT server applications to connect to BLE devices via the AP’s IoT radio using a southbound API. This service is generic to all BLE devices and is not limited to a specific device class.
An access point can connect to one BLE device at a time using BLE connect. Before connecting to another BLE device an existing connections has to be disconnected.
Note:
BLE connect using the southbound API is only supported using the internal IoT radio.
Note:
Starting with ArubaOS/Instant OS 8.8.0.0 BLE security (authentication/encryption) has been added to the BLE connect service. BLE security is only supported on the AP-5xx BLE5/802.15.4 (Gen2) IoT radio.
For details about the available BLE connect service please refer to the Aruba IoT Server Interface Guide.
BLE connect is enabled for the selected BLE device class in the iot transport profile configuration and requires the server connection type Telemetry-Websocket beeing selected.
Serial-data
Serial-data forwarding is used to support 3rd party IoT radio solutions connected via the AP USB port. When the 3rd party IoT radio is plugged into the USB port, it presents itself as a USB-to-serial device to the AP.
The serial data sent by the 3rd party radio to the AP is encapsulated in the Aruba IoT server interface protocol to/from the IoT backend system. The server can also send serial data to the AP, which will be forwarded to the 3rd party device.
Note:
Serial-data forwarding is only available when using the IoT server connection type Telemetry-Websocket.
Serial data forwarding is enabled using the device class serial-data in the iot transport profile configuration.
ZigBee socket device
ZigBee socket device (ZSD) service is a generic approach used for enabling ZigBee applications using the Aruba IoT radio Gen2.
Sending/receiving ZigBee application data using the ZigBee socket device (ZSD) service requires the configuration of one or multiple ZigBee socket device profiles which define the inbound and outbound sockets used by the respective ZigBee application.
- Inbound sockets
- Defines Zigbee application protocol layer (APL) packets received by the AP from ZigBee devices via the ZigBee radio
- Data is forwarded to the remote ZigBee application server via the Aruba IoT interface
- Outbound sockets
- Defines Zigbee application protocol layer (APL) packets received by the AP form the ZigBee application server via the Aruba IoT interface
- Data is forwarded to ZigBee devices via the ZigBee radio
A ZigBee socket profile definition consists of four items:
- source endpoint
- destination endpoint
- profile ID
- cluster ID
Different ZigBee services have different socket definitions, may be even for inbound and outbound connections.
Only the Aruba IoT radios Gen2 supports the ZigBee protocol and provides the coordinator function to establish a ZigBee network. The ZigBee service profile defines the respective ZigBee network parameters.
ZigBee socket device (ZSD) service is enabled using the device class zsd in the iot transport profile configuration. In addition one or multiple ZigBee socket device profiles have to be defined and assigned in the iot transport profile configuration.
Note:
The ZigBee socket device (ZSD) service is only available when using the IoT server connection type Telemetry-Websocket.
Details about the required configuration steps are describe in the chapter ZigBee configuration.
Device Class Filter
Device class filters are used to enabled specific IoT transport services over an IoT server connection and to control the amount of IoT data transferred on an Aruba infrastructure by using input/output filtering.
Every device class applies to a specific input filter on the IoT connectivity (radio-side) e.g., filtering BLE devices added to the BLE table and an output filter on the IoT server-side connection e.g., filtering which IoT data is forwarded to the remote server.
Note:
Concurrent input/output filtering can be disabled if required. In that case for example an AP could hold all seen BLE devices in its BLE table but only reports specific BLE devices to the remote server determined by the output filter. Please refer to the Aruba IoT documentation for details.
Multiple supported device classes can be enabled in the iot transport profile configuration to enable multiple IoT transport services over a single server connection.
Note:
A maximum of 16 devices classes can be enabled per iot transport profile.
Device class filter are grouped into the following categories.
BLE device class filter
For every supported BLE device vendor, identified by the Bluetooth SIG member list, a dedicated BLE device class is defined. One ore more BLE device classes can be selected in an iot transport profile to enable IoT transport services for the respective BLE vendor.
The special device class unclassified enables BLE telemetry reporting for unknown/unsupported BLE vendor devices.
The special device class all enables BLE telemetry reporting for all BLE device classes including unclassified BLE devices.
Wi-Fi device class filter
The device class wifi-assoc-sta and wifi-unassoc-sta enables the Wi-Fi telemetry transport service.
The device class wifi-tag enables the Wi-Fi RTLS data forwarding transport service.
USB/3rd party device class filter
The device class serial-data enables the serial-data forwarding to support 3rd party IoT radio solutions
ZigBee socket device class filter
The device class zsd enables the ZigBee socket device transport service to enable ZigBee applications.
Data content filters
In addition to filter for specific device classes it possible to filter the forwarded IoT data content before being sent to the remote Iot system.
General data filter
-
Data Filter
This is a list of data fields to be suppress in the telemetry reports. The data filter is a string that is a comma separated list of index-paths. Each index path refers to the field numbers in the Aruba IoT Protobuf Specification. For example, the value “3.3, 3.12” would suppress the ‘reported.model’ field and the ‘reported.beacons’ field in the telemetry reports. -
Device Count
Only sends the count of device types, e.g. iBeacon, Wi-Fi clients, seen by an AP in the telemetry reports, but not the actual device information of those devices. Supported device counts are defined in the Aruba IoT Protobuf Specification.
BLE data filter
- RSSI Reporting Format
For the BLE RSSI values being send in the telemetry reports five different RSSI reporting formats are supported. The four reporting formats are:- Average - The average RSSI over the reporting interval will be reported.
- Last - Only the last RSSI value that was seen by the device will be reported.
- Max - The max RSSI value that was seen over the reporting interval will be reported only. This max value resets each telemetry reporting interval and will be updated accordingly.
- Bulk - The last 20 RSSI values that were seen by the device since the previous telemetry report will be reported in an array format.
- Smooth - A single smoothed out RSSI value will be reported for each telemetry report. This is done by attempting to remove outliers from the RSSI values received by the AP.
- Environment Type
Five different pre-defined environment types are supported to help adjust RSSI based distance calculation to better fit the environment in which the BLE devices are operating in. For best results, the value that closest corresponds to the environment in which BLE is operating should be chosen.- auditorium
- office
- outdoor
- shipboard
- warehouse
- custom (see custom fading factor for details)
-
Custom Fading Factor
If the pre-defined environment type offsets do not properly fit the environment, a custom fading factor can be configured by setting the environment type to custom. This field accepts integer values in the range of 10 to 40. -
Cell Size Filter
A proximity-based filter that will only report devices that are found to be within an “x” meter radius around the access point. This distance is calculated with an algorithm based off the RSSI value. The default value for this field is “0”, which translates to the cell size filter being disabled. This field accepts integer values from 2 to 100 and the units are meters. -
Movement Filter
This filter is active when the cell size filter is also configured. When this filter is enabled, devices will only be reported if the difference between their current and prior distance is more than the configured filter value. For example, if the movement filter is configured to be 2 meters, a device that is calculated to have moved 1 meter will not be reported, while a device that moves 5 meters will be reported. The default value for this field is “0”, which corresponds to the movement filter being disabled. This field accepts integer values from 2 to 30, and the units are meters. -
Age Filter
The Age Filter is used to only report devices the AP has received an update (either BLE advertisement or scan response) in the configured time. For instance, if the age filter is set to 30 seconds, only devices which have been heard in the last 30 seconds will be reported. If there is a device that received an update 45 seconds before, this device will not be reported. The default value for this field is “0”, which corresponds to the age filter being disabled. This field accepts integer values from 30 to 3600, and the units are seconds. - BLE Vendor Filter
The BLE Vendor Filter allows to input Bluetooth SIG Vendor IDs and/or freeform vendor name strings, which will be used to filter the devices being reported. If this is configured, the only devices that will be reported are the devices that match the configured Vendor ID or Vendor Name.
The vendor ID is a 2-byte hexadecimal value preceding with 0x in 0xABCD format. The vendor name is a string that can be either a full vendor name (example:Aruba) or a substring of the actual vendor name (example:Aru) and can be case-insensitive.
The vendor filter accepts up to five combinations of vendor names or vendorIDs separated by commas, for example:- Aruba,Favendo,HanVit,SoluM,ABB
- 0xABCD,0xBCDE,0xCDEF,0xDEF0,0xEF01
- Aruba,0xABCD,Favendo,0xBCDE,HanVit
If more than one vendor name or vendorID is configured, then any of the matching vendor names or vendorIDs in the vendor filter is applied. A device is reported only if the vendor data or vendor name field is not empty and matches the vendor information configured. If the vendor field is not populated for the devices, the IoT devices are reported because there is not matching vendor filter in the IoT transport profile.
-
UUID Filter (iBeacon)
A list of UUIDs to filter the devices included in the reports. Applies only to iBeacon devices. -
UID Namespace Filter (Eddystone)
A list of UID namespaces to filter devices included in the reports. Applies only Eddystone-UID devices -
URL Filter (Eddystone)
A list of URL strings to filter devices included in the reports. Applies only Eddystone-URL devices. The string listed here can be a partial URL strings. - BLE data forwarding - per frame filtering
When BLE data forwarding is enabled, the raw payload contained within a BLE packet is forwarded to the configured server. The per frame filtering knob is a modifier on top of the BLE data forwarding knob. When only BLE data forwarding is enabled, all BLE packets for a device having a known device class filter label are forwarded.
For example: If a device advertises an iBeacon frame and an Eddystone frame and in the transport profile the iBeacon device class has been selected only, then for this device both iBeacon and Eddystone frames are forward.
If per frame filtering is enabled in addition to the BLE data forwarding , then only the raw payloads from the iBeacon frames will be forwarded.
Configuration
In this chapter the ArubaOS/Aruba Instant configuration steps are described to setup the Aruba infrastructure for IoT solutions using ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.8.0.0 or higher.
Note:
For Aruba Instant deployments managed via Aruba Central currently only template based configuration is supported.
The Aruba Instant configuraiton described in this chapter can be applied using Aruba Central configuration templaes to manage the IoT configuration of cloud-based Aruba infrastrucure deployments.
The configuration of Aruba IoT integrations consists of two main steps:
- IoT radio-side configuration
- IoT server-side configuration
Depending on respective IoT solution different configuration settings are required.
In the table below the required configuration items for step 1 and step 2 per IoT solution are listed:
| IoT solution | Step 1) IoT radio-side configuration | Step 2) IoT server-side configuration |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi solutions | Enable Wi-Fi radios (access or monitor mode) | iot transport profile |
| BLE solutions | iot radio profile | iot transport profile |
| ZigBee solutions | iot radio profile + zigbee service profile + zigbee socket device profile | iot transport profile |
| ZigBee solutions (ASSA-ABLOY) | iot radio profile + zigbee service profile | iot transport profile |
| USB/3rd party: USB-to-serial solutions | (optional) USB ACL profile/USB profile | iot transport profile |
| USB/3rd party: USB-to-ethernet solutions | (optional) USB ACL profile/USB profile | Wired-Port profile |
| USB/3rd party: SES Imagotag ESLs | (optional) USB ACL profile/USB profile + SES Imagotag ESL configuration | SES Imagotag ESL configuration |
Note:
The IoT radio settings for USB/3rd party radios are controlled on the 3rd party system, if any, and there is no configuration required on the Aruba side. The only exception is the SES Imagotag ESL configuration which controls the ESL radio channel.Which USB device are allowed to connect to an access point can be controlled using the AP USB device management.
For details about the different configuration steps requried to setup the IoT solutions layed out in the table above see the following chapters as well as the configuratoin examples chapter.
IoT radio profile
iot radio-profile’s are used to configure the Aruba IoT radio mode, BLE and/or ZigBee, and the respective mode settings. An iot radio-profile can either be applied to an internal or external radio instance.
The iot radio-profile also controls the AP’ BLE console settings.
The following table lists the available iot radio-profile parameters and their description:
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant | Description |
|---|---|---|
iot radio-profile <iot-profile-name> | iot radio-profile <iot-profile-name> | Name of the radio profile |
radio-instance <internal, external> | radio-instance <internal, external> | Type of the radio the profile applies to. Available options are: - internal - applies to the internal radio of the AP (default) - external - applies to the external radio that is connected over the USB port of the AP |
radio-firmware <firmware> | radio-firmware <firmware> | Firmware that is applied to the radio. Available options: - default - default firmware gets applied |
radio-mode <mode> | radio-mode <mode> | Radio mode to be enabled. Available options are: - None - Radio disabled (default) - ble - BLE (tx/rx) enabled - zigbee - ZigBee enabled - “ble zigbee” - BLE (tx-only) and ZigBee enabled concurrently |
ble-opmode <opmode> | ble-opmode <opmode> | BLE operation mode to be enabled. This parameter is available only when radio-mode is set to ble or “ble zigbee”.Available options are: - beaconing - BLE (tx) beaconing enabled using the iBeacon protocol (default) - scanning - BLE (rx) scanning enabled - “beaconing scanning” - BLE (tx/rx) beaconing and scanning enabled concurrently (default - does not show up in the configuration!) |
ble-console <console-mode> | ble-console <console-mode> | BLE console mode to be enabled. BLE console provides console access to the AP over BLE. This parameter is available only when radio-mode is set to ble or “ble zigbee”.Available options are: - dynamic - Enables BLE console automatically - on - BLE console enabled - off - BLE console disabled (default) |
ble-txpower <txpower> | ble-txpower <txpower> | BLE tx power in dBm to be used. This parameter is available only when radio-mode is set to ble or “ble zigbee”.- Value range: -20 … 4, (default: 0) |
zigbee-opmode <opmode> | zigbee-opmode <opmode> | ZigBee operation mode to be used. This parameter is available only when radio-mode is set to zigbee or “ble zigbee”.Available options are: - coordinator - Radio works as ZigBee coordinator (default) |
zigbee-channel <channel> | zigbee-channel <channel> | Channel to be used. This parameter is available only when radio-mode is set to zigbee or “ble zigbee”.Available options are: - auto - Selects the channel automatically (default) - Value range: 11 … 26 - Specifies the channel manually |
Additional CLI parameters:
clone- Copy data from anotheriot radio profile(ArubaOS only)no- Delete a command from the profile
Note:
The defaultble-opmode beaconing scanningdoes not show up in the configuration. Using the “beaconing scanning” parameter is only required to change the configuration formble-opmode beaconingorble-opmode scanningback to the default.If the
radio-modeis set to “ble zigbee” only BLE (tx) beaconing is supported, regardless of theble-opmodesetting.
An iot radio-profile is enabled using the following command:
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant |
|---|---|
iot useTransportProfile <iot-profile-name> | iot use-radio-profile <iot-profile-name> |
In addition to enabling the iot radio-profile it has to be assigned to an AP group in ArubaOS/controller based deployments using the following configuration:
ap-group <ap-group-name>
iot radio-profile <iot-profile-name>
For details about the ap-group configuration refer to the ArubaOS CLI Reference - ap-group.
Note:
Multipleiot radio-profile’s can be configured but a maximum of two, one internal and one external can be enabled per access point (Aruba Instant) or access point group (ArubaOS).
IoT transport profile
The iot transportProfile defines the IoT server connectivity settings using the Aruba IoT server interface.
The following table lists the available iot transportProfile parameters and their description:
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
iot transportProfile <transport-profile-name> | iot transportProfile <transport-profile-name> | Name of the transport profile | |
| Server connection settings | |||
serverType <type> | endpointType <type> | The type of IoT server the transport profile connects to. Available options are listed in the table Aruba IoT server interface - connection types. The default type is Meridian-Beacon-Management. | |
serverURL <URL> | endpointURL <URL> | IoT server connection URL used to connect to the remote server. This parameter is not available when Server type is set to Azure-IoTHub. Valid input values have to start with: - http(s):// - for server connection type Telemetry-https using HTTP (un-encrypted) or HTTPS(encrypted) connections - ws(s):// for server connection type Telemetry-Websocket using web socket (ws) or secure web socket (wss) connections | |
proxy server <ip/fqdn>[proxy user <username> password <password>] | proxyserver <ip/fqdn> <port> [<username> <password>] | Configures an optional proxy server to be used to establish the IoT server connection through. Optional proxy server authentication with username/password is supported. Available options are: - ip/fqdn - Proxy server ip address or full qualified domain name - port - Proxy server port - username - Proxy authentication username - password - Proxy authentication password | |
| n/a | vlan <vlanid> | Configures the uplink VLAN being used for IoT server connectivity. Only supported on Aruba Instant. Available options: - vlan id - VLAN id of uplink VLAN | |
| Reporting frequency settings | |||
reportingInterval <seconds> | transportInterval <seconds> | Configures the reporting interval (in seconds) for IoT transport services and vendor specific connections that support periodic reporting. The valid/supported value range depends on the configured serverType/endpointType and is listed in Aruba IoT server interface - connection types. | |
| Authentication/Authorization settings | |||
authentication-mode <mode> | authentication-mode <mode> | Configures the OAuth2 authentication mode to be used for the server connection. Available options are: - none - Authentication is disabled and a static access token is used for authorization (default) - password - Authentication using username/password - client-credentials - Authentication using client_id/client secret | |
authenticationURL <URL> | authenticationURL <URL> | Configures the authentication server URL. This parameter only applies if authentication-mode is set to password or client-credentials.Only encrypted connections are allowed starting with https://. | |
accessToken <token> | endpointToken <token> | Configures the static access token used for authorization. This parameter is only applicable when authentication-mode is set to none.Input values: - token - String, base64 characters only. | |
clientID <client_id> | endpointID <client_id> | Client identifier string that is used by the IoT server to identify the connecting Aruba infrastructure. This parameter only applies if serverType/endpointType is set to Meridian-Asset-Tracking, Telemetry-Https or Telemetry-Websocket.This parameter is required when authentication-mode is set to client-credentials for OAuth2 client_id/secret authentication.Input values: - client_id - string, 1-100 characters | |
client-secret <password> | client-secret <client-secret> | Configures the password for Oauth2 client_id/secret authentication. This parameter is required when authentication-mode is set to client-credentials. | |
username <username> | username <username> | Configures the username for username/password authentication. This parameter only applies if authentication-mode is set to password. | |
password <password> | password <password> | Configures the password for username/password authentication. This parameter only applies if authentication-mode is set to password. | |
accessID <assa-abloy-access-id> | accessID <assa-abloy-access-id> | Configures the Assa-Abloy accessID for the vendor specific connection type Assa-Abloy. This parameter only applies if serverType/endpointType is set to Assa-Abloy.In addition the configuration of the parameters username and password is required. | |
azure-dps-auth-type group-enrollment symmetric-key <key> | azure-dps-auth-type group-enrollment symmetric-key <key> | Configures the authentication type and credentials for the Azure Device Provisioning Service (DPS). Currently the only supported authentication type is group-enrollment using a symmetric-key. Available options are: - key - Azure symmetric group key. Requires the configuration of parameter azure-dps-id-scope.This parameter only applies if serverType/endpointType is set to Azure-IoTHub. | |
azure-dps-id-scope <scope-id> | azure-dps-id-scope <scope-id> | Configures the Azure Device Provisioning Service (DPS) enrollment group scope-id. Available options are: - scope-id - Azure DPS enrollment group scope-id. Requires the configuration of parameter azure-dps-auth-type.This parameter only applies if serverType/endpointType is set to Azure-IoTHub. | |
| Device filter settings | |||
deviceClassFilter <device-class> | payloadContent <device-class> | Configures a list of supported device classes to be included in telemetry reports or data forwarding to the remote IoT server. For details see Device Class Filter. A maximum of 16 devices classes can be enabled per iot transport profile. | |
| Wi-Fi specific settings | |||
rtlsDestMAC <MAC-address> | rtlsDestMAC <MAC-address> | Sets the destination MAC address filter for RTLS tags device class. This parameter only applies if serverType/endpointType is set to Telemetry-Websocket and the deviceClassFilter wifi-tag is selected to enable the Wi-Fi RTLS data forwarding transport service. | |
| ZigBee specific settings | |||
ZSDFilter <zigbee-socket-device-profile>...ZSDFilter <zigbee-socket-device-profile> | ZSDFilter <zigbee-socket-device-profile>,...,<zigbee-socket-device-profile> | Assigns a list of zigbee-device-socket-profiles to filter the allowed zigbee socket devices (ZigBee applications) forwarded by the transport profile. This parameter only applies if serverType/endpointType is set to Telemetry-Websocket and the deviceClassFilter zsd is selected to enable the ZigBee socket device transport service. | |
| General data content filter settings | |||
data-filter <data-id-list> | data-filter <data-id-list> | Configures a list of data points to filter from periodic telemetry reports before sending to the remote IoT server. The data fields refer to the field numbers in the Aruba IoT Protobuf Specification. This parameter only applies to IoT transport services that support periodic reporting. | |
deviceCountOnly | deviceCountOnly | Enables to send only the aggregated device type counts per configured device class. This parameter only applies to IoT transport services that support periodic reporting. | |
| BLE data content filter settings | These parameters only apply to BLE related device classes and transport services and if serverType/endpointType is set to Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket or Azure-IoTHub | ||
rssiReporting <format> | rssiReporting <format> | Set the preferred RSSI format BLE telemetry reporting. Available options are: - average - RSSI averaged over the reporting period (default) - bulk - Last 20 RSSI values seen by the device since the previous reporting interval - last - Last RSSI value seen by the device - max - Maximum RSSI measured over the reporting period - smooth - Smoothed RSSI measured over the reporting period | |
environmentType <type> | environmentType <type> | Set the working environment type for RSSI based BLE distance calculation.. Available options are: - auditorium - Auditorium environment - custom - Custom environment, set custom fading factor using customFadingFactor- office - Office environment (default) - outdoor - Outdoor environment - shipboard - Shipboard environment - warehouse - Warehouse environment | |
customFadingFactor <factor> | customFadingFactor <factor> | This parameter sets a custom fading factor the BLE distance calculation. This parameter only applies if environmentType is set to custom.Input values: Range: 10-40 | |
cellSizeFilter <cellsize> | cellSizeFilter <cellsize> | Sets a proximity filter specified in meters. Devices outside the cell will not be reported. Setting to 0 disables the cell size filter. Range: - Aruba Instant: 0 to 255 m - ArubaOS: 2 to 100 m Default: 0 | |
movementFilter <threshold> | movementFilter <threshold> | Filters devices that do not change distance. Specified in meters. Applicable only if a cellSizeFilter is set.Setting to 0 disables the movement filter. Range: - Aruba Instant: 0 to 255 m - ArubaOS: 2 to 30 m m Default: 0 | |
ageFilter <timeout> | ageFilter <timeout> | Sets a timeout for inactive devices. Devices without activity in the specified time frame will not be reported. Setting to 0 disables the ageFilter filter. Range: 30 to 3600 seconds Default: 0 | |
vendorFilter <vendor-list> | vendorFilter <vendor-list> | Specifies a list of Bluetooth SIG vendor IDs or vendor names. Only devices that match the configured Vendor ID or Vendor Name will be reported. Input value: - vendor-list - max 5 vendor IDs or vendor names, example: “0x011B,0x004C,Google” | |
uuidFilter <uuid-list> | uuidFilter <uuid-list> | Specifies a list of iBeacon UUIDs to filter devices included in the reports. This parameter only applies if the deviceClassFilter is set to ibeacon.Input value: - uuid-list - max 10 UUIDs, example: “xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx,yyyyyyyy-yyyy-yyyy-yyyy-yyyyyyyyyyyy” | |
uidNamespaceFilter <uid-list> | uidNamespaceFilter <uid-list> | Specifies a list of Eddystone-UID namespaces to filter devices included in the reports. This parameter only applies if the deviceClassFilter is set to eddystone.Input value: - uid-list - max 10 UUIDs, example: “707cc5b4983477cb3e77,707cc5b49883477cb3e7” | |
urlFilter <url-list> | urlFilter <url-list> | Specifies a list of Eddystone-URL strings to filter devices included in the reports. This parameter only applies if the deviceClassFilter is set to eddystone.Input value: - url-list - max 10 URLs, partial URL strings are allowed, example: “https://www.arubanetworks.com/iot,https://www.hpe.com” | |
bleDataForwarding | bleDataForwarding | Enable BLE data forwarding for all known BLE device classes. Default: disabled | |
perFrameFiltering | perFrameFiltering | Enables per frame BLE data filtering. If this option is enabled the transport profile filters are applied to each BLE frame rather than on the BLE device as a whole. This parameter only applies if bleDataForwarding is enabled.Default: disabled | |
| AP-group assignment | |||
include-ap-group <ap-group> | n/a | Applies one ore multiple AP groups to the transport profile. Only supported on ArubaOS. Required input values: - ap-group - AP group name |
Additional CLI parameters:
clone- Copy data from anotheriot transport profile(ArubaOS only)no- Delete a command from the profile
An iot transportProfile is enabled using the following command:
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant |
|---|---|
iot useTransportProfile <transport-profile-name> | iot useTransportProfile <transport-profile-name> |
Note:
Multiple transport profiles can be configured, but a maximum of 4 transport profiles can be enabled per access point (Aruba Instant) or access point group (ArubaOS).
AP USB device management
AP USB device management controls connected USB devices using USB profiles and USB ACL profiles. An USB ACL profile is assigned to an AP or AP group using an USB profile.
USB ACL profile
An USB ACL profile consists of one or more permit/deny rules for supported USB vendor-product names. An USB ACL profile includes an implicit deny-all at then end. An USB profile with an undefined USB ACL profile applies a permit-all by default.
Note:
Up to 16 USB ACL profiles are supported.
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant | Description |
|---|---|---|
ap usb-acl-prof <usb-acl-profile-name> | usb acl-profile <usb-acl-profile-name> | Name of the USB ACL profile |
rule vendor <vendor-name> action <permit/deny> | rule <vendor-name> <permit/dena> | Configure an ACL rule for a supported USB vendor-name. Available options are: - vendor-name - USB vendor name, All allows all supported vendors Available action value to perform if the vendor-name matches. Available options are: - deny - Access to USB device is denied - permit - Access to USB device is refused |
Note:
Theshow usb supported vendor-productcommand lists the supported USB vendor-names on Aruba Instant APs.
USB profile
An USB profile binds a specific USB ACL profile ton an AP or AP group.
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant | Description |
|---|---|---|
ap usb-profile <usb-profile-name> | usb profile <usb-profile-name> | Name of the USB profile |
usb-acl-profile <usb-acl-profile-name> | usb-acl <usb-acl-profile-name> | Assigns an previously defined USB profile to the USB profile. Available options are: - usb-acl-profile-name - Name of the USB ACL profile |
An USB profile is bound to an AP or AP group using the following commands:
ArubaOS
ap-group <ap-group-name>
usb-profile <usb-profile-name>
For details about the ap-group configuration refer to the ArubaOS CLI Reference - ap-group.
Aruba Instant
usb-profile-binding <usb-profile-name>
For details about the usb-profile-binding configuration refer to the Aruba CLI Reference - USB profile binding.
Examples:
ArubaOS
ap usb-acl-prof "UsbAclProf1"
rule vendor All action permit
!
ap usb-profile "UsbProf1"
usb-acl-profile "UsbAclPro1"
!
ap-group "ApGroup1"
usb-profile "UsbProf1"
!
Aruba Instant
usb acl-profile "UsbAclProf1"
rule All permit
exit
usb profile "UsbProf1"
usb-acl "UsbAclProf1"
exit
usb-profile-binding "UsbProf1"
Wired-Port profile
A wired port profile configures the USB port on the AP as a wired ethernet port. It allows to configure all aspects of the ethernet connectivity of the USB device including the following:
- Wired port settings (speed, duplex, …)
- VLAN assignment
- Network authentication settings (MAC-Auth, 802.1x, …)
- ACL or Aruba user role assignment
- Forwarding mode (tunneled, bridged) - ArubaOS-only
An wired port profile is bound to an AP or AP group using the following commands:
ArubaOS
ap-group <ap-group-name>
enet-usb-port-profile <wired-port-profile-name> (default: shutdown)
For details about the ap-group configuration refer to the ArubaOS CLI Reference - ap-group.
Aruba Instant
enet-usb-port-profile <wired-port-profile-name>
For details about the wired profile configuration refer to the ArubaOS CLI Reference - Wired profile.
Examples:
ArubaOS
ip access-list session allowall
any any any permit
ipv6 any any any permit
!
ip access-list session apprf-iot-device-sacl
!
user-role iot-device
access-list session global-sacl
access-list session apprf-iot-device-sacl
access-list session allowall
!
aaa profile "iot-wired_aaa_prof"
initial-role "iot-device"
!
ap wired-ap-profile "USB-to-ethernet-wiredApProf1"
wired-ap-enable
switchport access vlan 192
!
ap wired-port-profile "USB-to-ethernet-wiredPortProf1"
wired-ap-profile "USB-to-ethernet-wiredApProf1"
aaa-profile "iot-wired_aaa_prof"
!
ap-group "ApGroup1"
enet-usb-port-profile "USB-to-ethernet-wiredPortProf1"
!
Aruba Instant
wlan access-rule "USB-to-ethernet-wiredPortProf1"
index 1
rule any any match any any any permit
exit
wired-port-profile "USB-to-ethernet-wiredPortProf1"
switchport-mode access
allowed-vlan 192
no shutdown
access-rule-name "USB-to-ethernet-wiredPortProf1"
type employee
exit
enet-usb-port-profile "USB-to-ethernet-wiredPortProf1"
SES Imagotag ESL configuration
SES-Imagotag’s Electronic Shelf Label system uses a vendor-specific USB integration with the Aruba infrastructure using a dedicated set of configuration commands. In ArubaOS the SES-Imagotag configuration is enabled in the ap system-profile where Aruba Instant uses an sesimagotag-esl-profile.
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant | Description |
|---|---|---|
ap system-profile <ap-system-profile-name> | n/a | Name of the ap system-profile. Only supported on ArubaOS. Required input values: - ap-system-profile-name - AP system profile name |
| n/a | sesimagotag-esl-profile | Adds a SES-Imagotag ESL configuration profile. Only supported on Aruba Instant. |
sesImagotag-esl-channel <esl-channel> | sesImagotag-esl-channel <sl-channel> | The the radio channel of SES-Imagotag ESL radio. Available options are: - esl-channel - Range [0-10], 127 is ESL-server managed channel. Note: ArubaOS: If no ESL channel is configured the AP will select a channel automatically at boot time (but not automatic change later). Aruba Instant: A static channel or 127 has to be set manually. There is no auto channel selection on Aruba Instant. |
sesImagotag-esl-radio-coexistence | sesImagotag-esl-radio-coexistence | Enables the coexistence function between the SES-Imagotag ESL radio and the AP 2.4G Wi-Fi radio. When ESL radio tries to transmit packets the Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz radio is suspected for milliseconds to reduce interference. (Default: Enabled) |
sesImagotag-esl-server <FQDN> | sesImagotag-esl-server <FQDN> | Adds the FQDN of SES-Imagotag ESL server. FQDN setting has a higher priority than sesImagotag-esl-serverip if both are confiugured.Available options are: - FQDN - FQDN of the SES-Imagotag ESL server. |
sesImagotag-esl-serverip <ip-address> | sesImagotag-esl-serverip <ip-address> | Configures the ip address of the SES-Imagotag ESL server. Available options are: - ip-address - SES-Imagotag ESL server ip address |
sesImagotag-esl-tls-auth | sesImagotag-esl-tls-auth | Enables TLS authentication of the AP with the SES-Imagotag ESL server. The AP uses the factory default TPM certificate to autheitcated itself to the SES server and use the pre-loaded SES server’s trusted root certificate to validate the SES server certificate (Default: Disabled). |
sesImagotag-esl-tls-fqdn-verify | sesImagotag-esl-tls-fqdn-verify | Enables TLS certificate verification for the SES-Imagotag ESL server connection checking the configured FQDN against the TLS certificate presented by the SES-Imagotag server during connection establishment. Only applies if sesImagotag-esl-server <FQDN> is configured to use the SES cloud server.(Default: Disabled) |
Please find an example configuration here
ZigBee configuration
This secion describes the required configuration for ZigBee based solutions via the Aruba IoT radio Gen2 using the ZigBee socket device transport service.
Configuring a ZigBee solution requires the following setps:
1) Configuring an iot radio-profile
2) Configuring a zigbee service-profile 3) Configuring a zigbee socket-device-profile 4) Configuring an iot transportProfile
Note:
Assa-Abloy is currently the only supported vendor specific ZigBee solution using a vendor specific server connection type and not using the generic Zigbee socket device framework. Therefore step 3)zigbee socket-device-profileconfugration is NOT required for this solution. Please see the Assa-Abloy configuration exmaple for details.
ZigBee service profile
The zigbee service-profile determines the Zigbee network settings if ZigBee has been enabled in the iot radio-profile configuration.
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant | Description |
|---|---|---|
zigbee service-profile <profile-name> | zigbee service-profile <profile-name> | Name of the Zigbee service-profile. |
panid <panid> | panid <panid> | Sets the ZigBee pernsonal network identifier (PAN ID). Available options are: - auto - automatically selects a PAN ID (default) - [0000-FFF0] - hexadecimal PAN ID |
permit-joining {off, on} | permit-joining {off, on} | Enables or disables joining permission of new devices to the APs ZigBee network permanently. Available options are: - off - permanent joinging disabled (default) - on - permanent joining enabled Note: To allow devices to join in case joining is disabled see Permit ZigBee device joining |
radio-instance {all, external, internal} | radio-instance {all, external, internal} | Determines the IoT ZigBee radio instance the ZigBee service profile should be used with. Available options are: - all - applies the service-profile to internal and external IoT radios (default) - external - applies the servcie profile to external radio’s only - internal - applies the service-profile to internal radios only. |
security {disable, enable} | security {disable, enable} | Enables or disables ZigBee security. Available options are: - enable - enables ZigBee security (default) - disable - disables ZigBee security |
Additional CLI parameters:
clone- Copy data from anotherzigbee service-profile(ArubaOS only)no- Delete a command from the profile
A zigbee service-profile is bound to an AP or AP group using the following commands:
ArubaOS
ap-group <ap-group-name>
zigbee service-profile <profile-name>
For details about the ap-group configuration refer to the ArubaOS CLI Reference - ap-group.
Aruba Instant
zigbee use-service-profile <profile-name>
Permit ZigBee device joining
If permit-joining is disabled in the zigbee service-profile, which is the default setting, new clients can only join an APs ZigBee radio when it is temporarily permitted. Temporarily permitting joining is enabled using the zigbee-init-action command permit-joining.
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant | Description |
|---|---|---|
ap zigbee-init-action permit-joining {ap-name, ip-addr, ipv6-addr} <ap-name, ip-addr, ipv6-addr> radio <radio-addr> restart [<duration>] | zigbee-init-action permit-joining radio <radio-addr> restart [<duration>] | Opens the APs ZigBee radio for new zigBee device to join. Available options: - radio-addr - ZigBee radio MAC address or all - duration - 60 - 600 seconds, time window to allow joining, default: 600 s Available options (ArubaOS-only): - ap-name, ip-addr, ip6-addr - AP name or IP to execture the command on |
ap zigbee-init-action permit-joining {ap-name, ip-addr, ipv6-addr} <ap-name, ip-addr, ipv6-addr> radio <radio-addr> stop | zigbee-init-action permit-joining radio <radio-addr> stop | Closes the APs ZigBee radio for new ZigBee devices imidiately. Available options: - radio-addr - ZigBee radio MAC address or all - duration - 60 - 600 seconds, time window to allow joining, default: 600 s Available options (ArubaOS-only): - ap-name, ip-addr, ip6-addr - AP name or IP to execture the command on |
ZigBee socket-device-profile
The zigbee socket-device-profile profile defines the inbound and outbound sockets of a ZigBee application using the zigbee socket device (ZSD) service.
| ArubaOS | Aruba Instant | Description |
|---|---|---|
zigbee socket-device-profile <socket-device-profile-name> | zigbee socket-device-profile <socket-device-profile-name> | Name of the Zigbee socket-device-profile. |
zigbee socket-inbound-profile <inbound-socket-profile-name>or zigbee socket-outbound-profile <outbound-socket-profile-name> | n/a | Adds an inbound or outbound socket profile entry to the socket-device-profile (ArubaOS only).- Name - name of the inbound/outbound socket profile Note: In ArubaOS inbound/outbound socket profiles are explicitley defined while in Aruba Instant inbound/outbound socket entries are added directly (see next). |
source_endpoint <source_endpoint>endpoint <endpoint>profile <profile>cluster <cluster> [aps-ack] | <inbound, outbound> <source_endpoint> <endpoint> <profile> <cluster> [aps-ack] | Adds the zigbee socket device profile parameters. Available options: - inbound/outbound - socket direction (Aruba Instant only) - source_endpoint - ZigBee application soruce endpoint, range [1, 254] - endpoint - ZigBee application destination endpoint, range [1, 254] - profile - ZigBee application profile ID, range [0x0000, 0x7FFF], [0xC000, 0xFFFF] - cluster - ZigBee application cluster ID, range [0x0000, 0x7FFF], [0xFC00, 0xFFFF] - aps-ack - Enables acknowledgement of ZigBee APS packets, optional, only applicable if socket direction is set to outbound |
The zigbee socket-device-profile is assigned to the iot transportProfile using the ZSDFilter command.
Note:
A maximum of 8 inbound and 4 outbound socket are supported per ZigBee socket device profile while a maximum of 4 ZigBee socket device profiles are supported per IoT transport profile.
Plesae see Generic ZSD solution for a configuration example unsing the the ZigBee socket device transport service.
Configuration Examples
This chapter provides configuration examples for supported IoT solutions and use cases on an Aruba infrastructure.
IoT-Utilities App
IoT-Utilities App (ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.7.x.x)
This example shows the configuration to setup an Aruba IoT demo using the IoT-Utilities app using ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.7.x.x.
ip-address- has to be replaced with the IP address of the mobile device the IoT-Utilities app is running on. The current IP address used by the app is shown in the IoT-Utilties Dashboard - Server control panel status.port- has to be replaced with the apps port number configured in the apps IoT-server settings. The default value is 5443.client-id- optional: should be replaced with a custom client identifier to uniquily identify the connecting Aruba infrasturcture within the IoT-Utilities app.username- has to be replaced with the apps authentication username configured in the apps IoT-server settingspassword- has to be replaced with the apps authentication password configured in the apps IoT-server settingsap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
Note:
The self-signed server certificate or the trusted root CA certificate used by the IoT-Utilities app has to be installed on the Aruba infrastructure for the sercure web socket server connection to be established. The self-signed certificate can be downloaded either via the IoT-Utilties Dashboard - Certificate Control Panel or using the apps web dashboard.
Please see the Aruba CLI Reference - Importing Certificates for details about how to install the downloaded certificate on the Aruba infrastructure.
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode none ble
ble-opmode scanning
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "IoT-Utilities-App"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "wss://<ip-address>:<port>/telemetry"
authenticationURL "https://<ip-address>:<port>/auth"
clientId <client-id>
username <username>
password <password>
deviceClassFilter all
deviceClassFilter wifi-tags
deviceClassFilter wifi-assoc-sta
deviceClassFilter wifi-unassoc-sta
deviceClassFilter serial-data
deviceClassFilter unclassified
reportingInterval 30
rssiReporting last
bleDataForwarding
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "IoT-Utilities-App"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode ble
ble-opmode scanning
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-scan"
iot transportProfile "IoT-Utilities-App"
endpointURL "wss://<ip-address>:<port>/telemetry"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
authenticationURL "https://<ip-address>:<port>/auth"
endpointID <client-id>
username <username>
password <password>
payloadContent all
payloadContent unclassified
payloadContent serial-data
payloadContent wifi-tags
payloadContent wifi-assoc-sta
payloadContent wifi-unassoc-sta
transportInterval 30
ageFilter 30
bleDataForwarding
rssiReporting last
exit
iot useTransportProfile "IoT-Utilities-App"
IoT-Utilities App (ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.8.x.x or higher)
This example shows the configuration to setup an Aruba IoT demo using the IoT-Utilities app using ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.8.x.x or higher.
ip-address- has to be replaced with the IP address of the mobile device the IoT-Utilities app is running on. The current IP address used by the app is shown in the IoT-Utilties Dashboard - Server control panel status.port- has to be replaced with the apps port number configured in the apps IoT-server settings. The default value is 5443.client-id- should be replaced with a custom client identifier to uniquily identify the connecting Aruba infrasturcture within the IoT-Utilities app.secret- has to be replaced with the apps Static access token configured in the apps IoT-server settingsap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
Note:
The self-signed server certificate or the trusted root CA certificate used by the IoT-Utilities app has to be installed on the Aruba infrastructure for the sercure web socket server connection to be established. The self-signed certificate can be downloaded either via the IoT-Utilties Dashboard - Certificate Control Panel or using the apps web dashboard.
Please see the Aruba CLI Reference - Importing Certificates for details about how to install the downloaded certificate on the Aruba infrastructure.
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode none ble
ble-opmode scanning
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "IoT-Utilities-App"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "wss://<ip-address>:<port>/telemetry"
authentication-mode client-credentials
authenticationURL "https://<ip-address>:<port>/auth"
clientId <client-id>
client-secret <secret>
deviceClassFilter all
deviceClassFilter wifi-tags
deviceClassFilter wifi-assoc-sta
deviceClassFilter wifi-unassoc-sta
deviceClassFilter serial-data
deviceClassFilter unclassified
reportingInterval 30
rssiReporting last
bleDataForwarding
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "IoT-Utilities-App"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode ble
ble-opmode scanning
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-scan"
iot transportProfile "IoT-Utilities-App"
endpointURL "wss://<ip-address>:<port>/telemetry"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
authentication-mode client-credentials
authenticationURL "https://<ip-address>:<port>/auth"
endpointID <client-id>
client-secret <secret>
payloadContent all
payloadContent unclassified
payloadContent serial-data
payloadContent wifi-tags
payloadContent wifi-assoc-sta
payloadContent wifi-unassoc-sta
transportInterval 30
ageFilter 30
bleDataForwarding
rssiReporting last
exit
iot useTransportProfile "IoT-Utilities-App"
Wi-Fi solutions
Wi-Fi client tracking solution
This example shows the required configuration to enable Wi-Fi telemetry.
fqdn, ip-address- has to be replaced with the FQDN or IP address of the remote serveraccess-token- has to be replaced with the static access token used to connect to the remote serverclient-id- has to be replaced with the client identifier string that is used by the remote server to identify the connecting Aruba infrastructureap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
ArubaOS
iot transportProfile "Wi-Fi-telemetry"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "[ws|wss]://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
accessToken <access-token>
clientId <client-id>
deviceClassFilter wifi-assoc-sta
deviceClassFilter wifi-unassoc-sta
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "Wi-Fi-telemetry"
Aruba Instant
iot transportProfile "Wi-Fi-telemetry"
endpointURL "[ws|wss]://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
payloadContent wifi-assoc-sta
payloadContent wifi-unassoc-sta
endpointToken <access-token>
endpointID <client-id>
exit
iot useTransportProfile "Wi-Fi-telemetry"
Wi-Fi RTLS data forwarding solution
This example shows the required configuration to enable Wi-Fi RTLS data forwarding.
fqdn, ip-address- has to be replaced with the FQDN or IP address of the remote serveraccess-token- has to be replaced with the static access token used to connect to the remote serverclient-id- has to be replaced with the client identifier string that is used by the remote server to identify the connecting Aruba infrastructuremac-address- has to be replaced with the destination MAC address used by Wi-fi tagsap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
ArubaOS
iot transportProfile "Wi-Fi-RTLS"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "[ws|wss]://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
accessToken <access-token>
clientId <client-id>
deviceClassFilter wifi-tags
include-ap-group <ap-group>
rtlsDestMAC <mac-address>
!
iot useTransportProfile "Wi-Fi-RTLS"
Aruba Instant
iot transportProfile "Wi-Fi-RTLS"
endpointURL "[ws|wss]://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
payloadContent wifi-tags
endpointToken <access-token>
endpointID <client-id>
rtlsDestMAC <mac-address>
exit
iot useTransportProfile "Wi-Fi-RTLS"
BLE vendor specific solutions
Aruba Meridian Beacon Management
This example shows the required configuration to enable Aruba Meridian Beacon Management. For more details on the Aruba Meridian related confiugration please refer to the Aruba Meridian Online Documenation - Configure Aruba Hardware
access-token- has to be replaced with the static access token generated using the Meridian Beacon Management menuap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
Note:
Because theserverType/endpointType Meridian-Beacon-Managemenand thereportingIntervalof 600 s are the default values, they do not show up in the confiugration.
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
radio-mode none ble
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "Meridian-Beacon-Management"
serverURL "https://edit.meridianapps.com/api/beacons/manage"
accessToken <access-token>
deviceClassFilter aruba-beacons
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "Meridian-Beacon-Management"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
radio-mode ble
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
iot transportProfile "Meridian-Beacon-Management"
endpointURL https://edit.meridianapps.com/api/beacons/manage
endpointToken <access-token>
payloadContent managed-beacons
exit
iot useTransportProfile "Meridian-Beacon-Management"
Aruba Meridian Asset Tracking
This example shows the required configuration to enable Aruba Meridian Asset Tracking. For more details on the Aruba Meridian related confiugration please refer to the Aruba Meridian Online Documenation - Configure Aruba Hardware
Note:
The DigiCert root certificate has to be installed on the Aruba infrastructure when connecting the Meridian tags server. This is only required for the asset tracking tunnels to Meridian using WebSocket Secure (wss) protocol. Please see the Aruba CLI Reference - Importing Certificates for details.
Note: The Aruba Meridian Beacon Management configuration is required for both beacons management and asset tracking because it reports beacon and tag information such as hardware type, battery level, MAC address, uuid/major/minor, rssi, firmware, etc. to Meridian. Whereas the Aruba Meridian Asset Tracking only reports tag telemetry data to Meridian. So, whether you are doing beacons management or asset tracking, you must have a least the beacons management iot profile configured.
access-token- has to be replaced with the static access token generated using the Meridian Beacon Management menuclient-id- has to be replaced with the Meridian location id which can be found in the Meridian Editor settings pageap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
radio-mode none ble
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "Meridian-Beacon-Management"
serverURL "https://edit.meridianapps.com/api/beacons/manage"
accessToken <access-token>
deviceClassFilter aruba-beacons
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "Meridian-Beacon-Management"
!
iot transportProfile "Meridian-Asset-Tracking"
serverType Meridian-Asset-Tracking
serverURL "https://tags.meridianapps.com/api/v1beta1/streams/ingestion.start"
accessToken <access-token>
clientId <client-id>
deviceClassFilter aruba-beacons
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "Meridian-Asset-Tracking"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
radio-mode ble
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
iot transportProfile "Meridian-Beacon-Management"
endpointURL https://edit.meridianapps.com/api/beacons/manage
endpointToken <access-token>
payloadContent managed-beacons
exit
iot useTransportProfile "Meridian-Beacon-Management"
iot transportProfile "Meridian-Asset-Tracking"
endpointType Meridian-Asset-Tracking
endpointURL https://tags.meridianapps.com/api/v1beta1/streams/ingestion.start
endpointToken <access-token>
endpointID <client-id>
payloadContent managed-tags
transportInterval 5
exit
iot useTransportProfile "Meridian-Asset-Tracking"
ZF Openmatics
This example shows the required configuration to enable ZF Openmatics asset tracking.
username- has to be replaced with the login username for the ZF deTAGtive platformpassword- has to be replaced with the login password for the ZF deTAGtive platformap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
Note:
The DigiCert root certificate has to be installed on the Aruba infrastructure when connecting the ZF Openmatics deTAGtiv platform. Please see the Aruba CLI Reference - Importing Certificates for details.
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode none ble
ble-opmode scanning
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "ZF-Openmatics-deTAGtive"
serverType ZF-Openmatics
serverURL "https://app.detagtive.com/backend/"
username <username>
password <password>
reportingInterval 5
deviceClassFilter zf-tags
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "ZF-Openmatics-deTAGtive"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode ble
ble-opmode scanning
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-scan"
iot transportProfile "ZF-Openmatics-deTAGtive"
endpointURL https://app.detagtive.com/backend/
endpointType ZF
payloadContent zf-tags
username <username>
password <password>
transportInterval 5
exit
iot useTransportProfile "ZF-Openmatics-deTAGtive"
BLE telemetry solutions
iBeacon + Eddystone asset tracking
This example shows the required configuration to enable BLE telemety reporting for ibeacon and eddystone BLE devices for asset tracking and eddystone based sensor monitoring.
fqdn, ip-address, port, path- has to be replaced with the FQDN or IP address, optional port and path of the remote serveraccess-token- has to be replaced with the static access token used to connect to the remote serverclient-id- has to be replaced with the client identifier string that is used by the remote server to identify the connecting Aruba infrastructureap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode none ble
ble-opmode scanning
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "BLE-telemetry"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "[ws|wss]://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
accessToken <access-token>
clientId <client-id>
reportingInterval 1
deviceClassFilter ibeacon
deviceClassFilter eddystone
ageFilter 30
rssiReporting last
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "BLE-telemetry"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode ble
ble-opmode scanning
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-scan"
iot transportProfile "BLE-telemetry"
endpointURL "[ws|wss]://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
payloadContent ibeacon
payloadContent eddystone
endpointToken <access-token>
endpointID <client-id>
transportInterval 1
ageFilter 30
rssiReporting last
exit
iot useTransportProfile "BLE-telemetry"
HYPROS (ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.7.x.x)
This example shows the required configuration to enable the HYPROS tracking and tracing solutions integrartion using ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.7.x.x.
fqdn, ip-address, port, path- has to be replaced with the FQDN or IP address, optional port and path of the HYPROS serverclient-id- has to be replaced with the HYPROS customer client id consisting of:"<customer-name>-client"username- has to be replaced with the HYPROS server login usernamepassword- has to be replaced with the HYPROS server login passwordap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)interval- has to be replaced with a HYPROS deployment specific reporting intervaluuid-list- has to be replaced with a HYPROS deployment specific iBeacon UUID list to filter for, format:"xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx,yyyyyyyy-yyyy-yyyy-yyyy-yyyyyyyyyyyy"
Note:
The self-signed server certificate of the HYPROS server has to be installed on the Aruba infrastructure for the sercure web socket server connection to be established. Please see the Aruba CLI Reference - Importing Certificates for details.
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode none ble
ble-opmode scanning
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "HYPROS"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "wss://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
clientId <client-id>
username <username>
password <password>
reportingInterval <interval>
deviceClassFilter ibeacon
authenticationURL "https://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
uuidFilter <uuid-list>
ageFilter 30
rssiReporting last
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "HYPROS"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode ble
ble-opmode scanning
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-scan"
iot transportProfile "HYPROS"
endpointURL "wss://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
payloadContent ibeacon
endpointID <client-id>
username <username>
password <password>
transportInterval <interval>
uuidFilter <uuid-list>
ageFilter 30
authenticationURL "https://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
rssiReporting last
exit
iot useTransportProfile "HYPROS"
HYPROS (ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.8.x.x or higher)
This example shows the required configuration to enable the HYPROS tracking and tracing solutions integrartion using ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.8.x.x or higher.
fqdn, ip-address, port, path- has to be replaced with the FQDN or IP address, optional port and path of the HYPROS serverclient-id- has to be replaced with the HYPROS customer client id consisting of:"<customer-name>-client"secret- has to be replaced with the HYPROS server client credentialsap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)interval- has to be replaced with a HYPROS deployment specific reporting intervaluuid-list- has to be replaced with a HYPROS deployment specific iBeacon UUID list to filter for, format:"xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx,yyyyyyyy-yyyy-yyyy-yyyy-yyyyyyyyyyyy"
Note:
The self-signed server certificate of the HYPROS server has to be installed on the Aruba infrastructure for the sercure web socket server connection to be established. Please see the Aruba CLI Reference - Importing Certificates for details.
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode none ble
ble-opmode scanning
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "HYPROS"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "wss://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
clientId <client-id>
client-secret <secret>
reportingInterval <interval>
deviceClassFilter ibeacon
authenticationURL "https://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
authentication-mode client-credentials
uuidFilter <uuid-list>
ageFilter 30
rssiReporting last
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "HYPROS"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode ble
ble-opmode scanning
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-scan"
iot transportProfile "HYPROS"
endpointURL "wss://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
payloadContent ibeacon
endpointID <client-id>
client-secret <secret>
transportInterval <interval>
uuidFilter <uuid-list>
ageFilter 30
authenticationURL "https://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
authentication-mode client-credentials
rssiReporting last
exit
iot useTransportProfile "HYPROS"
BLE data forwarding solutions
Azure IoT Hub (ble data)
This example shows the required configuration to enable BLE data forwarding for all supported BLE vendors to Azure IoT Hub.
scope-id- has to be replaced with Azure DPS enrollment group scope-idkey- has to be replaces with Azure symmetric group keyap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
Note:
bleDataForwardingis enabled by default for server typeAzure-IoTHuband cannot be disabled.
Caution:
Enabling the device class filterallwill enable BLE data forwarding of all knon/supported BLE vendor device classes. This could haveally increase the amount of data beeing forwarded to the remote server because all BLE advertisements and scan respsonse packets are forwarded in near real time.
It is recommended to use the BLE device class filter and BLE data filters to filter the data being forwarded.
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode none ble
ble-opmode scanning
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "Azure-IoT-Hub-ble-data"
serverType Azure-IoTHub
deviceClassFilter all
bleDataForwarding
azure-dps-id-scope <scope-id>
azure-dps-auth-type group-enrollment symmetric-key <key>
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "Azure-IoT-Hub-ble-data"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-scan"
radio-mode ble
ble-opmode scanning
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-scan"
iot transportProfile "Azure-IoT-Hub-ble-data"
endpointType Azure-IoTHub
payloadContent all
bleDataForwarding
azure-dps-id-scope <scope-id>
azure-dps-auth-type group-enrollment symmetric-key <key>
exit
iot useTransportProfile "Azure-IoT-Hub-ble-data"
BLE connect solutions
ABB (ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.7.x.x)
This example shows the required configuration to enable the ABB Ability™ Smart Sensor integrartion using ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.7.x.x.
client-id- has to be replaced with the ABB Ability™ account organization IDusername- has to be replaced with the email address of the ABB Ability™ accountpassword- has to be replaced with the login password of the ABB Ability™ accountap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
Note:
The ABB Ability™ Smart Sensor integrartion is levaraging the BLE data forwarding service which is enabled by default for the device class ability-smart-sensor in ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.7.x.x. There is manual configuration supported for BLE data forwarding in this version.
Note:
The Baltimore CyberTrust Root certificate (BaltimoreCyberTrustRoot.crt.pem) has to be installed on the Aruba infrastructure when connecting the ABB Ability™ Smart Sensor platform. Please see the Aruba CLI Reference - Importing Certificates for details.
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
radio-mode none ble
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "ABB-Ability-Smart-Sensor"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "https://api.smartsensor.abb.com/v7/Auth/BearerOAuth2"
clientId <client-id>
username <username>
password <password>
reportingInterval 3600
deviceClassFilter ability-smart-sensor
authenticationURL "https://api.smartsensor.abb.com/v7/Auth/BearerOAuth2"
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "ABB-Ability-Smart-Sensor"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
radio-mode ble
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
iot transportProfile "ABB-Ability-Smart-Sensor"
endpointURL "https://api.smartsensor.abb.com/v7/Auth/BearerOAuth2"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
payloadContent ability-smart-sensor
endpointID <client-id>
username <username>
password <password>
transportInterval 3600
authenticationURL "https://api.smartsensor.abb.com/v7/Auth/BearerOAuth2"
exit
iot useTransportProfile "ABB-Ability-Smart-Sensor"
ABB (ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.8.x.x or higher)
This example shows the required configuration to enable the ABB Ability™ Smart Sensor integrartion using ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.8.x.x or higher.
client-id- has to be replaced with the ABB Ability™ account organization IDsecret- has to be replaced with the client credentials of the ABB Ability™ accountap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
Note:
The ABB Ability™ Smart Sensor integrartion is levaraging the BLE data forwarding service. Starting with ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.8.x.x or higher BLE data forwarding is disabled by default and has to be explicitely eanbled for the device class ability-smart-sensor.
When migrating form ArubaOS/Aruba Instant 8.7.x.x to 8.8.x.x the iot transport profile configuration has to be adapgted to continue to work!
Note:
The Baltimore CyberTrust Root certificate (BaltimoreCyberTrustRoot.crt.pem) has to be installed on the Aruba infrastructure when connecting the ABB Ability™ Smart Sensor platform. Please see the Aruba CLI Reference - Importing Certificates for details.
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
radio-mode none ble
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
!
iot transportProfile "ABB-Ability-Smart-Sensor"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "https://api.smartsensor.abb.com/v8/Auth/BearerOAuth2"
clientId <client-id>
client-secret <secret>
reportingInterval 3600
deviceClassFilter ability-smart-sensor
bleDataForwarding
authenticationURL "https://api.smartsensor.abb.com/v8/Auth/BearerOAuth2"
authentication-mode client-credentials
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "ABB-Ability-Smart-Sensor"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
radio-mode ble
exit
iot use-radio-profile "int-beacon-scan"
iot transportProfile "ABB-Ability-Smart-Sensor"
endpointURL "https://api.smartsensor.abb.com/v8/Auth/BearerOAuth2"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
payloadContent ability-smart-sensor
bleDataForwarding
endpointID <client-id>
client-secret <secret>
transportInterval 3600
authenticationURL "https://api.smartsensor.abb.com/v8/Auth/BearerOAuth2"
authentication-mode client-credentials
exit
iot useTransportProfile "ABB-Ability-Smart-Sensor"
USB vendor specific solutions
SES Imagotag
This example shows the required configuration to enable an SES-Imagotag ESL soulution on premise solution. All avaialbe confiugation options are descirbed in the SES Imagotag ESL configuration
<ip-address>- has to be replaced with the SES-Imagotag on-premises server IP address
ArubaOS
ap system-profile "iot-ap-system-prof"
sesImagotag-esl-serverip <ip-address>
sesImagotag-esl-channel 127
Aruba Instant
sesimagotag-esl-profile
sesImagotag-esl-serverip <ip-address>
sesimagotag-esl-channel 127
USB-to-ethernet solutions
Solu-M ESL
This example shows the required configuration to enable the Solu-M ESL soltuion.
vlan-id- has to be replaced with the desired access vlan id to be used for the ESL USB gatewayap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
Note:
The ArubaOS configuration tunnels the ESL USB gateway traffic to the Aruba controller into the vlanvlan-idcontrolled though the controller firewall.The Aruba Instant configration egress the ESL USB gateway traffic at the access point uplink port into the desired vlan (tagged). The AP’s uplink switche port has to allow the
vlan-idtagged.
ArubaOS
ap usb-acl-prof "Solu-M-USB-GW-acl"
rule vendor All action permit
!
ap usb-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW"
usb-acl-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW-acl"
!
ap-group <ap-group>
usb-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW"
!
ip access-list session allowall
any any any permit
ipv6 any any any permit
!
user-role Solu-M-USB-GW
access-list session allowall
!
aaa profile "Solu-M-USB-GW_aaa_prof"
initial-role "Solu-M-USB-GW"
!
ap wired-ap-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW-wiredApProf"
wired-ap-enable
switchport access vlan <vlan-id>
!
ap wired-port-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW-wiredPortProf"
wired-ap-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW-wiredApProf"
aaa-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW_aaa_prof"
!
ap-group <ap-group>
enet-usb-port-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW-wiredPortProf"
!
Aruba Instant
usb acl-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW-acl"
rule Solu-M-SLG-DM101 permit
exit
usb profile "Solu-M-USB-GW"
usb-acl "Solu-M-USB-GW-acl"
exit
usb-profile-binding "Solu-M-USB-GW"
wlan access-rule "Solu-M-USB-GW-wiredPortProf"
rule any any match any any any permit
exit
wired-port-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW-wiredPortProf"
switchport-mode access
allowed-vlan <vlan-id>
native-vlan <vlan-id>
no shutdown
access-rule-name "Solu-M-USB-GW-wiredPortProf"
type employee
exit
enet-usb-port-profile "Solu-M-USB-GW-wiredPortProf"
USB-to-serial solutions
EnOcean demo
This example shows the required configuration to enable the Aruba EnOcean Demo Kit.
ip-address- has to be replaced with the IP address of the windows client the demo software is running onap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
ArubaOS
iot transportProfile "EnOcean-Demo"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "ws://<ip-address>:8000/arubaws"
accessToken "1234567890"
clientId "ArubaController"
deviceClassFilter serial-data
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "EnOcean-Demo"
Aruba Instant
iot transportProfile "EnOcean-Demo"
endpointURL "ws://<ip-address>:8000/arubaws"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
payloadContent serial-data
endpointToken "1234567890"
endpointID "ArubaInstant"
exit
iot useTransportProfile "EnOcean-Demo"
Azure IoT Hub (serial-data)
This example shows the required configuration to enable serial-data forwarding to Azure IoT Hub.
scope-id- has to be replaced with Azure DPS enrollment group scope-idkey- has to be replaces with Azure symmetric group keyap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
Note:
bleDataForwardingis enabled by default for server typeAzure-IoTHuband cannot be disabled. But only enablingpayloadContent serial-dataeffectively disables all BLE device classes and therefore no BLE data is forwarded.
ArubaOS
iot transportProfile "Azure-IoT-Hub-serial-data"
serverType Azure-IoTHub
payloadContent serial-data
bleDataForwarding
azure-dps-id-scope <scope-id>
azure-dps-auth-type group-enrollment symmetric-key <key>
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "Azure-IoT-Hub-serial-data"
Aruba Instant
iot transportProfile "Azure-IoT-Hub-serial-data"
endpointType Azure-IoTHub
payloadContent serial-data
bleDataForwarding
azure-dps-id-scope <scope-id>
azure-dps-auth-type group-enrollment symmetric-key <key>
exit
iot useTransportProfile "Azure-IoT-Hub-serial-data"
ZigBee solutions
ASSA ABLOY
This example shows the required configuration to enable the ASSA ABLOY door-lock solution.
fqdn, ip-address- has to be replaced with the FQDN or IP address of the Assa-Abloy serverusername- has to be replaced with the username on the Assa-Abloy serverpassword- has to be replaced with the password of the Assa-Abloy serveraccessid- has to be replaces with the Assa-Abloy server access idap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "int-zb"
radio-mode none zigbee
!
zigbee service-profile "int-zb-no-sec-auto"
radio-instance internal
security disable
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "int-zb"
zigbee service-profile "int-zb-no-sec-auto"
!
iot transportProfile "Assa-Abloy"
serverType Assa-Abloy
serverURL "https://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
username <username>
password <password>
deviceClassFilter assa-abloy
include-ap-group <ap-group>
accessID <accessid>
!
iot useTransportProfile "Assa-Abloy"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile int-zb
radio-mode zigbee
exit
zigbee service-profile int-zb-no-sec-auto
security disable
iot transportProfile "Assa-Abloy"
endpointURL "httts://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
endpointType Assa-Abloy
payloadContent assa-abloy
username <username>
password <password>
accessID <accessid>
exit
iot use-radio-profile int-zb
zigbee use-service-profile int-zb-no-sec-auto
iot useTransportProfile "Assa-Abloy"
Generic ZSD solution
This example shows the required configuration to enable the ZigBee socket device (ZSD) service
fqdn, ip-address- has to be replaced with the FQDN or IP address of the remote serveraccess-token- has to be replaced with the static access token used to connect to the remote serverclient-id- has to be replaced with the client identifier string that is used by the remote server to identify the connecting Aruba infrastructureap-group- has to be replaced with the AP group name the configuration should be enabled on (multiple statements are required for multiple groups) (ArubaOS only)
ArubaOS
iot radio-profile "ext-zb"
radio-instance external
radio-mode none zigbee
!
zigbee service-profile "ext-zb-sec-auto"
radio-instance external
!
ap-group <ap-group>
iot radio-profile "ext-zb"
zigbee service-profile "ext-zb-sec-auto"
!
zigbee socket-inbound-profile "zb-in-prof-1"
cluster 2100
profile 0a1e
endpoint 242
source-endpoint 1
!
zigbee socket-inbound-profile "zb-in-prof-2"
cluster 1900
profile 0104
endpoint 11
source-endpoint 1
!
zigbee socket-outbound-profile "zb-out-prof-1"
cluster 0000
profile 0104
endpoint 11
source-endpoint 1
!
zigbee socket-outbound-profile "zb-out-prof-2"
cluster 0003
profile 0104
endpoint 11
source-endpoint 1
!
zigbee socket-outbound-profile "zb-out-prof-3"
cluster 0010
profile 0104
endpoint 11
source-endpoint 1
!
zigbee socket-outbound-profile "zb-out-prof-4"
cluster 01fc
profile 0104
endpoint 11
source-endpoint 1
!
zigbee socket-device-profile "zb-device-prof-1"
inbound "zb-in-prof-1"
outbound "zb-out-prof-1"
outbound "zb-out-prof-2"
!
zigbee socket-device-profile "zb-device-prof-2"
inbound "zb-in-prof-2"
outbound "zb-out-prof-3"
outbound "zb-out-prof-4"
!
iot transportProfile "ZSD"
serverType Telemetry-Websocket
serverURL "[ws|wss]://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
accessToken <access-token>
clientId <client-id>
deviceClassFilter ZSD
ZSDFilter "zb-device-prof-1"
ZSDFilter "zb-device-prof-2"
include-ap-group <ap-group>
!
iot useTransportProfile "ZSD"
Aruba Instant
iot radio-profile ext-zb
radio-instance external
radio-mode zigbee
exit
zigbee service-profile ext-zb-sec-auto
radio-instance external
zigbee socket-device-profile "zb-device-prof-1"
inbound 242 1 0a1e 2100
inbound 11 1 0104 1900
outbound 1 11 0104 0000
outbound 1 11 0104 0003
outbound 1 11 0104 0010
outbound 1 11 0104 01fc
exit
iot transportProfile "ZSD"
endpointURL "[ws|wss]://<fqdn|ip-address>[:<port>][<path>]"
endpointType telemetry-websocket
payloadContent zsd
endpointToken <access-token>
endpointID <client-id>
ZSDFilter "zb-device-prof-1"
exit
iot use-radio-profile ext-zb
zigbee use-service-profile ext-zb-sec-auto
iot useTransportProfile "ZSD"
Verification and troubleshooting
t.b.d.
Appendix
Aruba Reference Documentation
- ArubaOS 8.8 Online Documentation
- Aruba Instant 8.8 Online Documentation
- Aruba CLI Reference
- Aruba Central Online Documenation
Aruba CLI Reference - ap-group
Aruba CLI Reference - ap system-profile
Aruba CLI Reference - iot radio-profile
Aruba CLI Reference - iot transportProfile
Aruba CLI Reference - Data-Filter
Aruba CLI Reference - USB ACL profile
Aruba CLI Reference - USB profile
Aruba CLI Reference - USB profile binding
Aruba CLI Reference - Wired profile
- ArubaOS CLI Reference - Configuring the AP Wired Port Profile
- Aruba Instant CLI Reference - Configuring a Wired Profile
Aruba CLI Reference - ZigBee
- AurbaOS CLI Reference - ZigBee service-profile
- AurbaOS CLI Reference - ZigBee socket-device-profile
- AurbaOS CLI Reference - ZigBee socket-inbound-profile
- AurbaOS CLI Reference - ZigBee socket-outbound-profile
- Aruba Instant CLI Reference - ZigBee service-profile
- Aruba Instant CLI Reference - ZigBee socket-device-profile
- Aruba Instant CLI Reference - ZigBee suse-service-profile
Aruba Central Online Documentation - Configuring APs Using Templates
Aruba CLI Reference - Importing Certificates
Aruba IoT Basic Setup Guide
Aruba IoT Server Interface Guide
Aruba IoT Telemetry JSON Schema
- ArubaOS WLAN and InstantOS IoT Interface - JSON Schema Telemetry
- ArubaOS WLAN and InstantOS IoT Interface - JSON Telemetry Example
Aruba IoT Protobuf Specification
Azure IoT Hub Integration
Aruba Meridian Online Documenation - Configure Aruba Hardware
Aruba IoT server interface - connection types
Supported connection type list as of ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.8.0.0.
| Server connection type | Transport protocol | Data encapsulation | Authentication & Authorization | Supported report interval (in seconds) | Supported device class filter | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assa-Abloy | HTTPS | vendor specific | username/password, access_id | 1-3600 s, default: 600 | assa-abloy | Assa Abloy Visiononline server |
| Azure-IoTHub | AMQP over secure web socket | JSON | symmetric group key | n/a -telemetry reports are not supported | all BLE types, serial-data | Connect with Azure IoT Hub |
| Meridian-Beacon-Management | secure web socket (wss) | vendor specific | static access token | 10-600 s, default: 600 s | aruba-beacons | POST to a RESTful Meridian API |
| Meridian-Asset-Tracking | secure web socket (wss) | vendor specific | client_id/secret | 2-600 s, default: 5 s | aruba-tags | Stream data to Meridian WebSocket server |
| Telemetry-Https | HTTP, HTTPS | JSON | username/password, client_id/secret, static access token | 1-3600 s, default: 600 s | all BLE types, wifi-assoc-sta, wifi-unassoc-sta | POST Aruba IoT telemetry reports to HTTP server endpoint |
| Telemetry-Websocket | web socket (ws), secure web socket (wss) | Protocol Buffers (protobuf) | username/password, client_id/secret, static access token | 1-3600 s, default: 600 s | all BLE types, wifi-tags, serial-data, zsd (ZigBee) | Stream data payloads to Aruba IoT interface compatible web socket server |
| ZF-Openmatics | secure web socket (wss) | vendor specific | username/password | 5-600 s, default: 60 s | zf-tags | ZF Openmatics cloud management |
Supported IoT vendor/device class list
Device class list as of ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.8.0.0.
| Device class | IoT connectivity (radio) | Supported server connectivity | Minimum required SW version | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aruba-beacons | BLE | Meridian-Beacon-Management, Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.4.0.0 or higher | Forward Aruba beacon BLE device data payloads |
| aruba-tags | BLE | Meridian-Asset-Tracking, Telemetry-Https,Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.4.0.0 or higher | Forward Aruba tag BLE device data payloads |
| aruba-sensors | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.5.0.0 or higher | Forward Aruba sensor BLE device data payloads. This an Aruba specific BLE beacon format for telemetry reporting of multiple sensor values by BLE device implementing the Aruba sensor specification |
| ibeacon | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.4.0.0 or higher | Forward iBeacon BLE device data payloads Telemetry reporting of the following iBeacon data payloads is supported: - UUID - broadcasted Universally Unique Identifier - Major - broadcasted major id - Minor - broadcasting minor id |
| eddystone | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Azure-IoTHub, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.4.0.0 or higher | Forward Eddystone BLE device data payloads. Telemetry reporting of the following Eddystone data payloads is supported: - Eddystone-TLM - broadcasted telemetry (temperature, voltage) - Eddystone-URL - broadcasted URL addresses - Eddystone-UID - broadcasted beacons IDs |
| zf-tags | BLE | ZF-Openmatics or Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.3.0.0 or higher | Forward ZF-Openmatics tag BLE device data payloads |
| enocean-sensors | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.4.0.0 or higher | Forward EnOcean sensor BLE device data payloads |
| enocean-switches | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.4.0.0 or higher | Forward EnOcean switch BLE device data payloads |
| mysphera | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.6.0.0 or higher | Forward MySphera BLE device data payloads |
| ability-smart-sensor | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket | 8.6.0.0 or higher | Forward ABB sensor BLE device data payloads |
| sbeacon | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.6.0.0 or higher | Forward sBeacon(HID) BLE device data payloads |
| wiliot | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.7.0.0 or higher | Forward Wiliot BLE device data payloads |
| exposure-notification | BLE | Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.7.0.0 or higher | Forward Apple/Google exposure notification framework BLE device data payloads |
| blyott | BLE | Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.8.0.0 or higher | Forward Blyott BLE device data payloads |
| diract | BLE | Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.8.0.0 or higher | Forward Diract BLE device data payloads |
| BLE | Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.8.0.0 or higher | Forward Google BLE device data payloads | |
| gwahygiene | BLE | Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.8.0.0 or higher | Forward GWA Hygiene BLE device data payloads |
| minew | BLE | Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.8.0.0 or higher | Forward Ninew BLE device data payloads |
| onity | BLE | Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.8.0.0 or higher | Forward Onity BLE device data payloads |
| polestar | BLE | Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.8.0.0 or higher | Forward Polestar BLE device data payloads |
| unclassified | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.4.0.0 or higher | all BLE devices we don’t know |
| all | BLE | Telemetry-Https, Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.4.0.0 or higher | all BLE devices form known vendors |
| assa-abloy | ZigBee | Assa-Abloy | 8.6.0.0 or higher | Forwarding ASSA-ABLOY to Assa Abloy Visiononline server |
| zsd | ZigBee | Telemetry-Websocket | 8.7.0.0 or higher | Forwarding ZigBee data payloads to an ZigBee application server |
| serial-data | USB/3rd party | Telemetry-Websocket, Azure-IoTHub | 8.7.0.0 or higher | Forwarding serial data payloads of 3rd party USB extensions to an IoT system |
| wifi-assoc-sta | Wi-Fi | Telemetry-Websocket | 8.6.0.0 or higher | Forwarding Wi-Fi client RSSI information to 3rd party |
| wifi-unassoc-sta | Wi-Fi | Telemetry-Websocket | 8.6.0.0 or higher | Forwarding Wi-Fi client RSSI information to 3rd party |
| wifi-tags | Wi-Fi | Telemetry-Websocket | 8.6.0.0 or higher | Forwarding Wi-Fi tag data to 3rd party system |
Supported USB vendor list for IoT
IoT related supported USB vendor list as of ArubaOS/Aruba Instant version 8.8.0.0.
| Vendor | Minimum required AOS/Instant Version | Connection method | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SES Imagotag | 8.4.0.0 or higher | vendor-specific | ESL USB dongle (on-premise mgmt) |
| SES Imagotag | 8.8.0.0 or higher | vendor-specific | ESL USB dongle (cloud mgmt) |
| Solu-M | 8.5.0.0 or higher | usb-to-ethernet | ESL Solu-M USB Gen1 GW |
| Solu-M | 8.8.0.0 or higher | usb-to-ethernet | ESL Solu-M NEWTON USB Gen2 GW |
| Hanshow | 8.6.0.0 or higher | usb-to-ethernet | ESL USB dongle |
| AmberBox | 8.6.0.0 or higher | usb-to-ethernet | Gunshot detector |
| EnOcean | 8.7.1.0 or higher | usb-to-serial | EnOcean USB 800/900 MHz |
| Piera Systems | 8.8.0.0 or higher | usb-to-serial | Particulate Matter (PM) Detection |